Brain Surgery
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Number of days at hospital (Estimated) | 4-5 days |
| Number of days in India outside hospital (Estimated) | 2-3 weeks |
| Treatment’s Success Rate | 95% and above |
| Tests required to help assess the treatment | X-ray, regular blood tests and MRI in certain cases |
What is Brain surgery?
Brain surgery is a procedure that treats brain abnormalities or issues within your brain and the surrounding areas. The brain is part of your central nervous system. It controls your ability to speak, move, think and remember. Brain surgery treats underlying conditions in, on or around your brain without disrupting your body’s important functions.
Types of Brain Surgery
There are many types of brain surgery. Some of the most common include:
- Biopsy
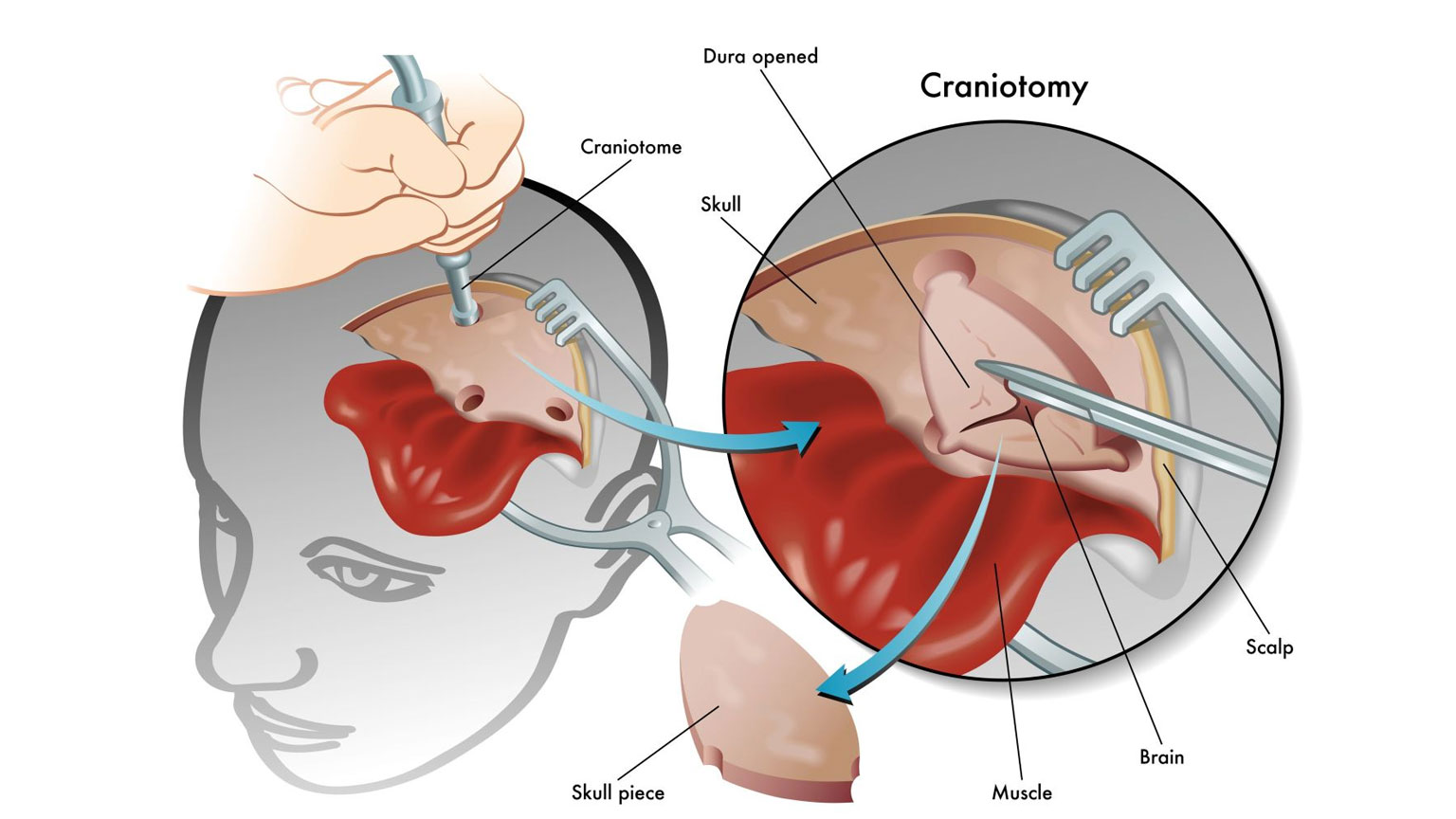
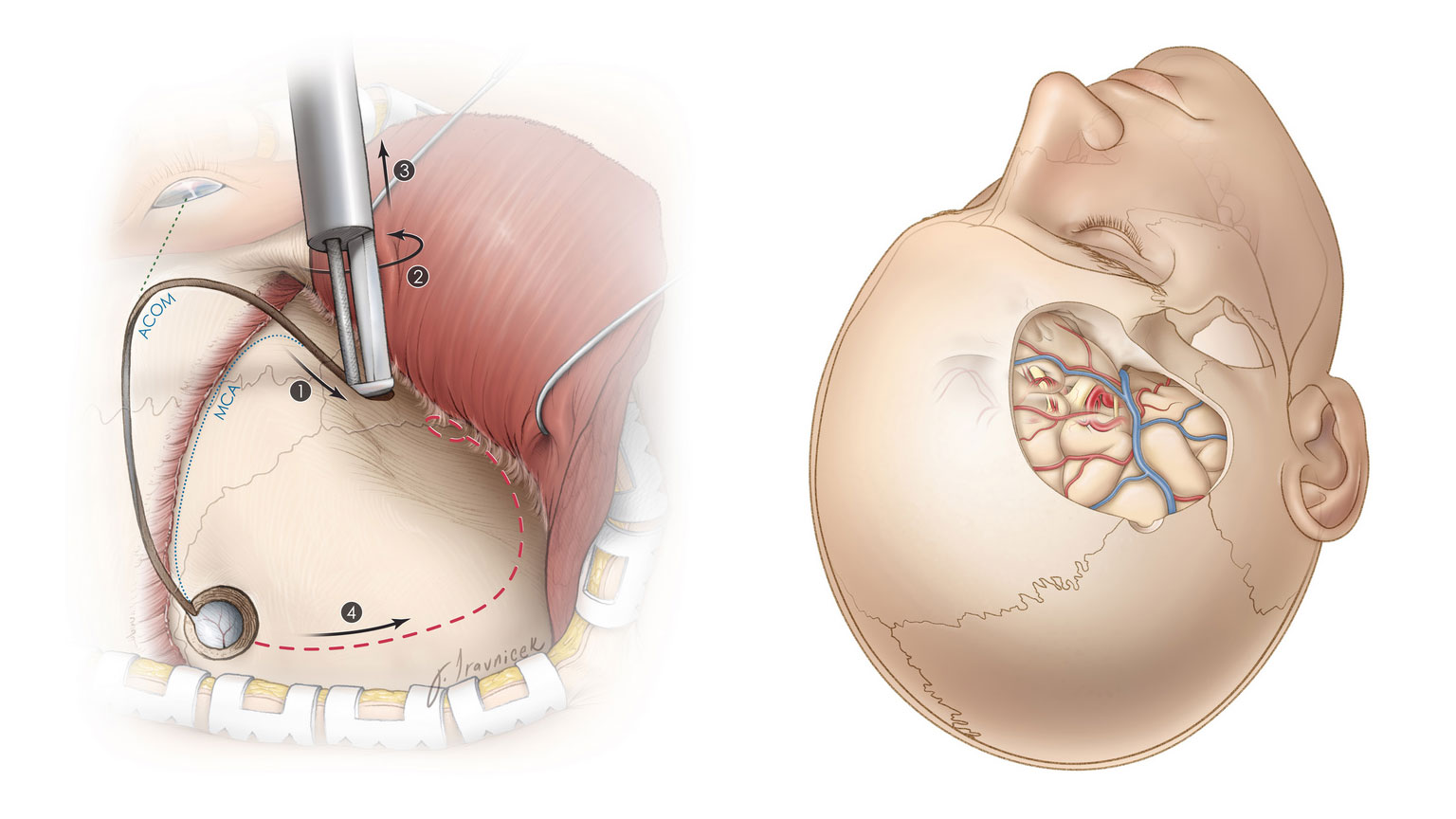
- Craniotomy
- Craniectomy
- Neuroendoscopy
- DBS
- Laser ablation
YThere are different types of biopsies. The difference between them is the way the surgeon does the biopsy. You might have:
- a biopsy as part of the operation to remove the tumour
- a needle biopsy
- an open biopsy
- a neuroendoscopy
- Removal of brain tumors (both malignant and benign).
- MRI or CT scans to locate the problem area precisely.
- Draining abscesses or treating brain infections.
- Risk of bleeding during or after the surgery.
- Severe head injuries that cause brain swelling.
- Risk of meningitis or other infections.
- Risk of hemorrhage during or after surgery.
- The bone flap (or a synthetic substitute) is reattached to the skull.
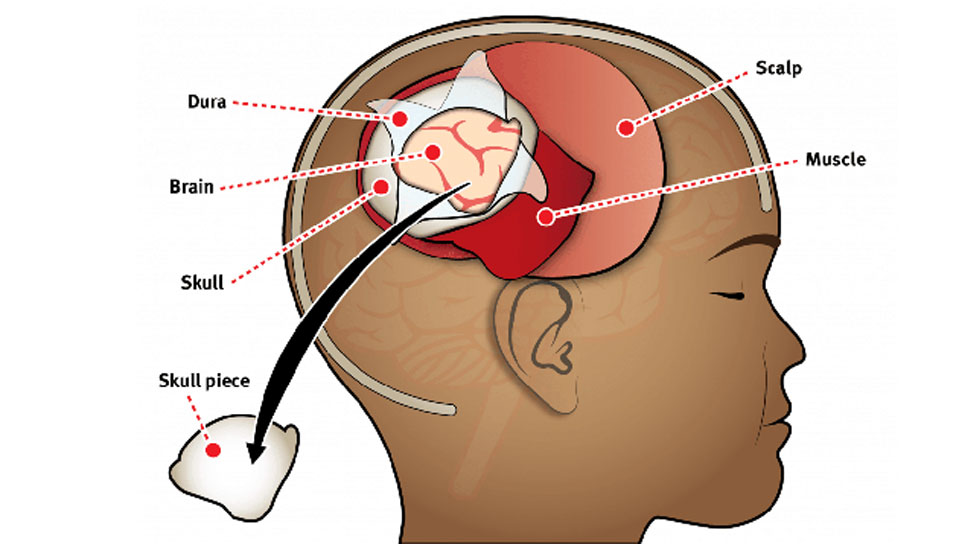
- Minimally Invasive: Small incisions, reduced trauma.
- Enhanced Visualization: Clear, magnified view of brain structures.
- Precision: Targeted removal or repair of brain tissue.
- Recovery: Shorter hospital stay, faster healing.
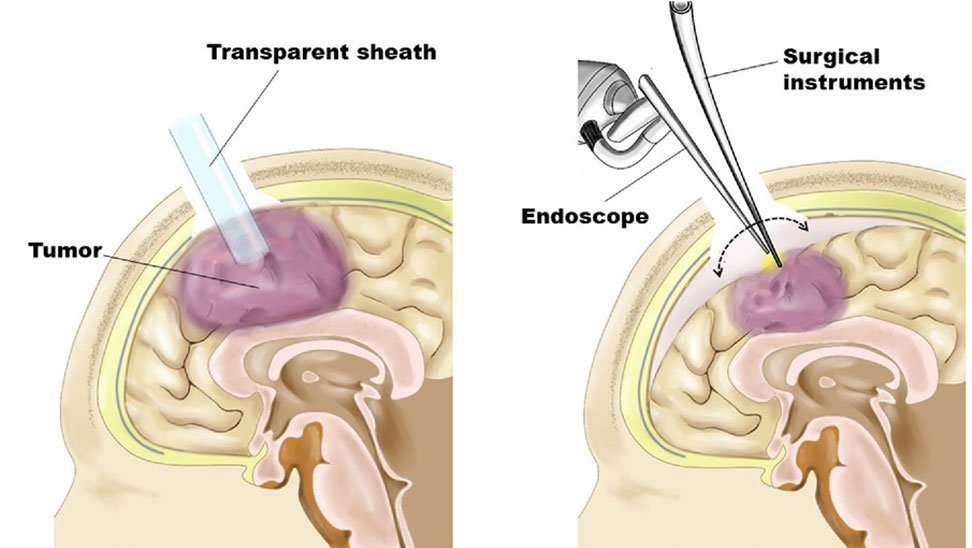
- Treats neurological conditions (e.g., Parkinson's).
- Implants electrodes in brain.
- Electrical stimulation alters brain activity.
- Reduces symptoms, improves quality of life.
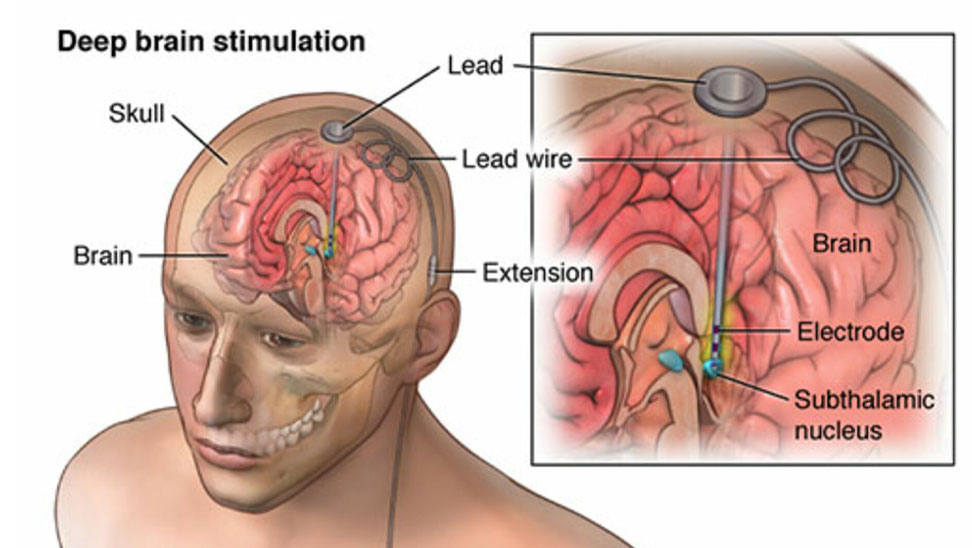
- Minimally Invasive: Small incision, reduced risk.
- Precision: Targeted removal of abnormal tissue.
- Heat Energy: Laser creates thermal ablation.
- Real-time Monitoring: MRI guidance ensures accuracy.
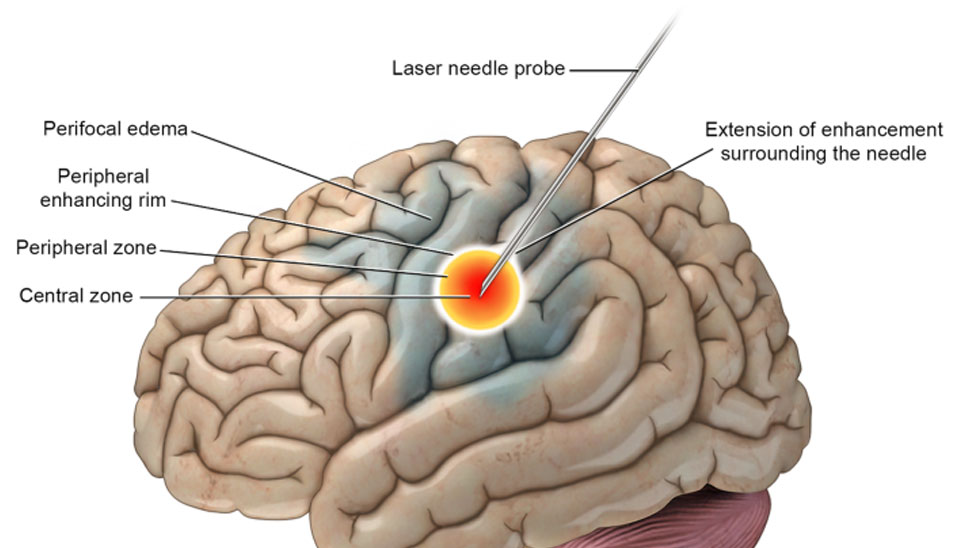
Who Require a Brain Surgery ?
- Brain Tumors: Both benign and malignant tumors may require surgical removal.
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Severe injuries may necessitate surgery to reduce swelling or remove damaged tissue.
- Vascular Disorders: Conditions like aneurysms or arteriovenous malformations may require surgical intervention.
- Epilepsy: Surgery may be considered for patients whose seizures are not controlled with medication.
- Hydrocephalus: Excess cerebrospinal fluid may require surgical shunting or treatment.
Tests Required For Brain Surgery
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Provides detailed images of brain structures.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Offers cross-sectional images for precise planning.
- EEG (Electroencephalogram): Measures electrical activity in the brain.
- Neuropsychological Testing: Assesses cognitive function and memory.
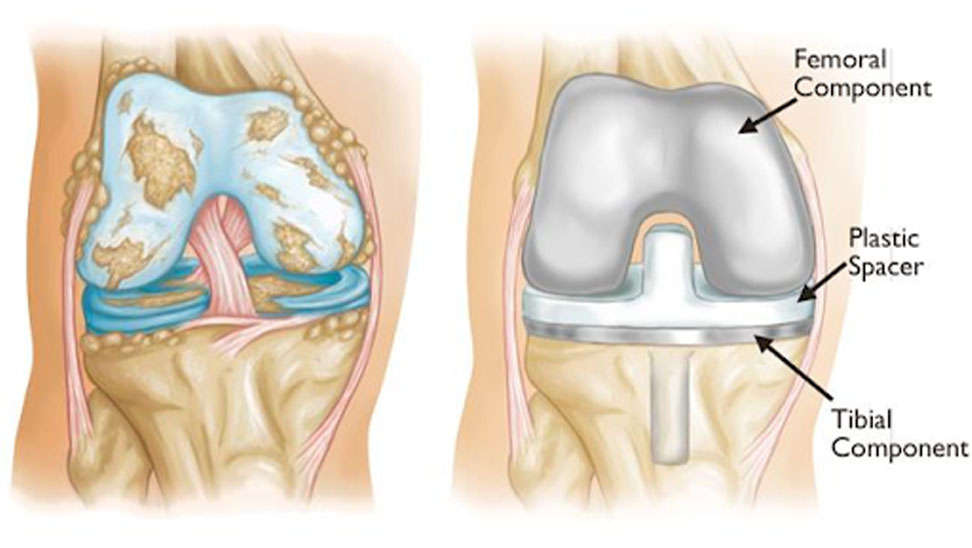
During The Knee Replacement Surgery
Following the incision, the surgeon carefully removes the damaged parts of the knee joint. The surgeon then places the prosthetic knee joint which is made up of metal and plastic.
After The Knee Replacement Surgery
A knee replacement surgery cannot be performed on an outpatient basis anywhere. It requires a hospital stay of three-four days. On the first day after surgery, the patient will meet with the physical therapist who will advise the patient to walk about with the help of crutches.
Physical therapy sessions following knee replacement surgery may be painful, but it is extremely important to follow them so that the new knees are able to function just as well as a healthy knee.
A Continuous Passive Motion machine (CPM) is used during one’s hospital stay. This device is attached to the affected leg and keeps surrounding areas of the knee in motion. This helps with speeding up recovery time and reducing post-operative complications.