Knee Replacement Surgery
| Particulars | Details |
|---|---|
| Number of days at hospital (Estimated) | 4-5 days |
| Number of days in India outside hospital (Estimated) | 2-3 weeks |
| Treatment’s Success Rate | 95% and above |
| Tests required to help assess the treatment | X-ray, regular blood tests and MRI in certain cases |
Knee Replacement Surgery in India
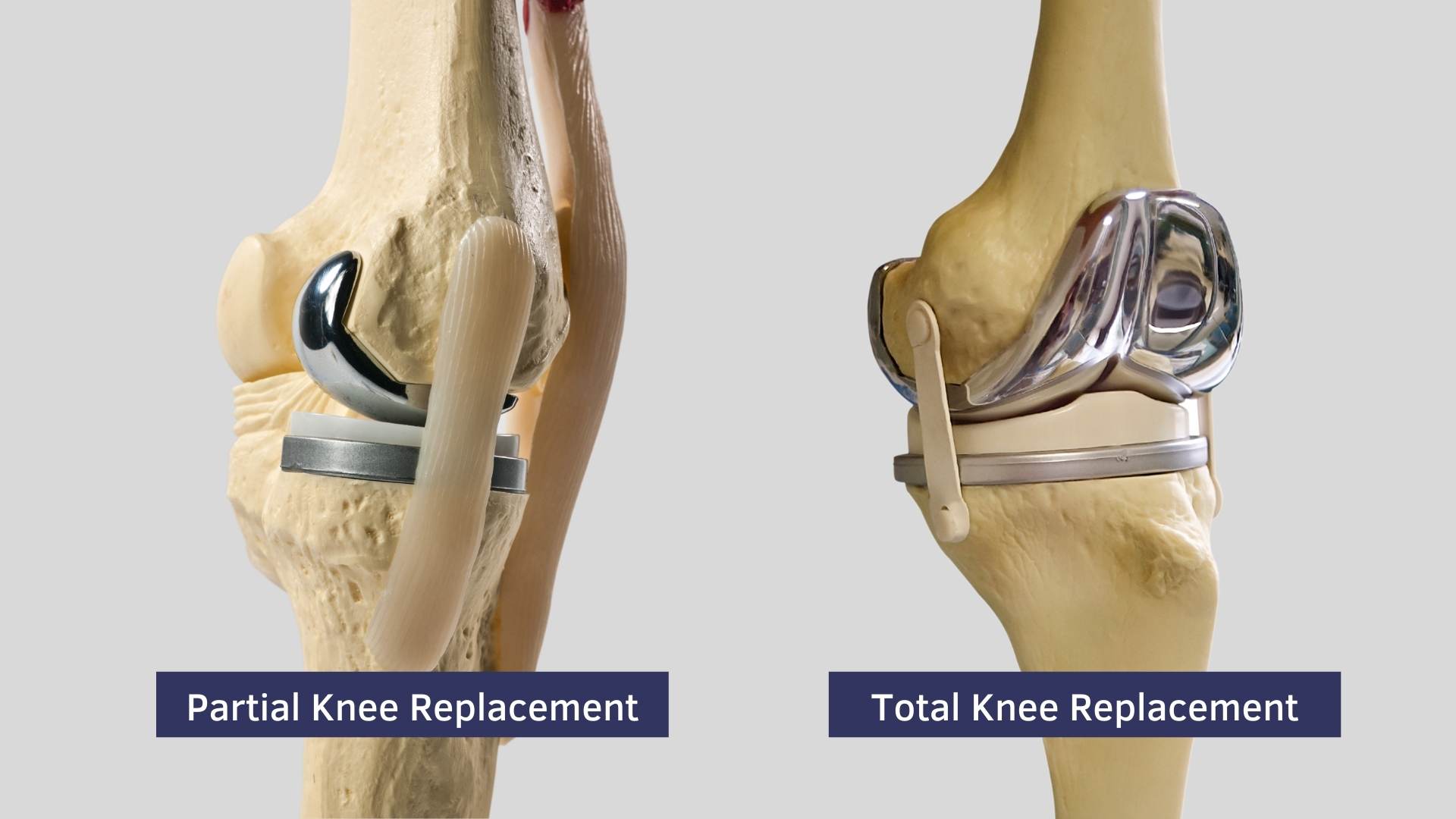
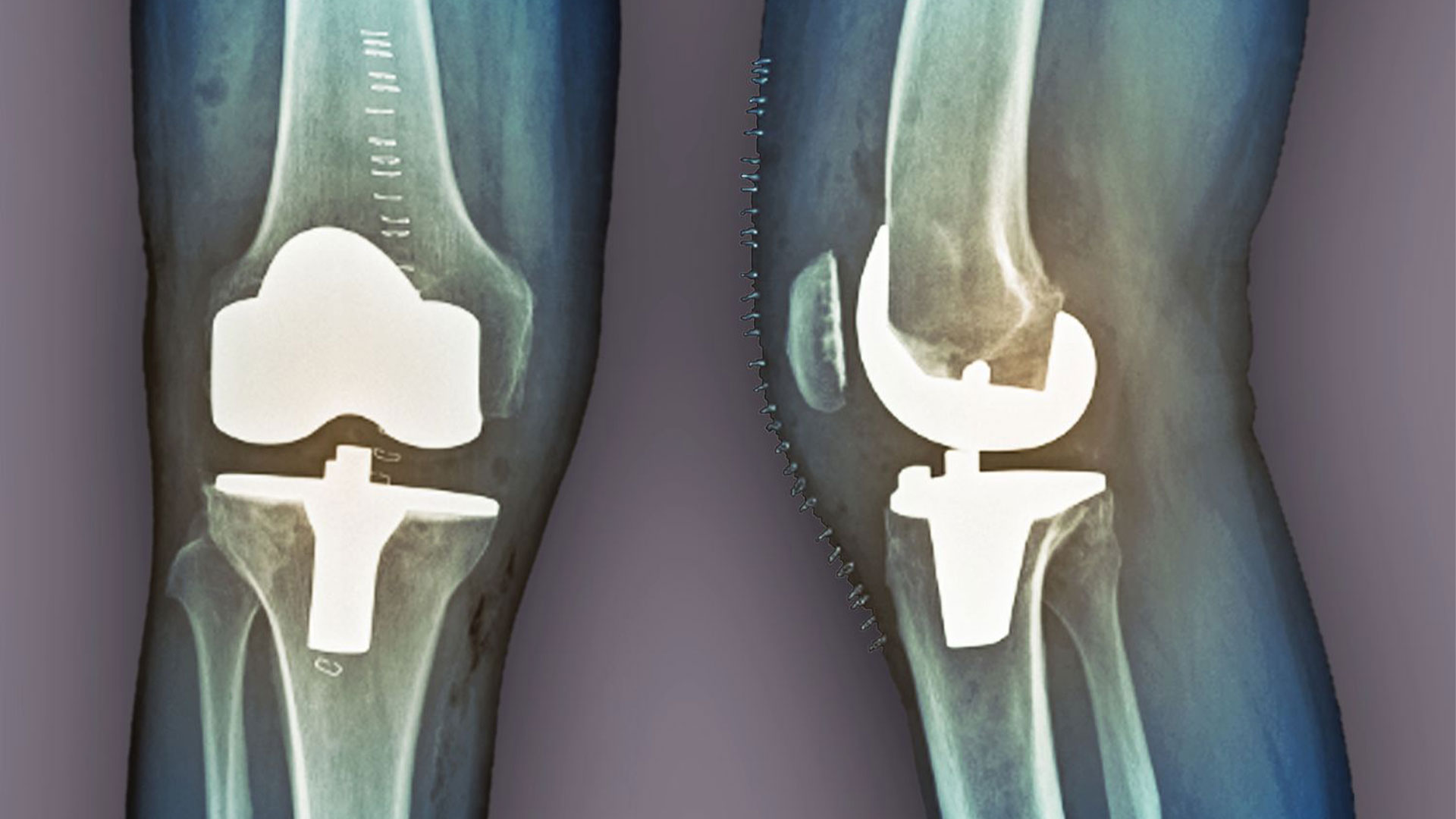
There are two types of knee replacement surgeries: total knee replacement and partial knee replacement. In total knee replacement surgery, both sides of the knee joint are replaced, while in partial knee replacement surgery, only one side of the knee joint is replaced.
The Knees
The knee joint consists of smaller bones, including the fibula and the patella (kneecap). Tendons link the knee joint to surrounding muscles, while ligaments connect the knee bones, providing stability and supporting the body’s balance.
Types of Knee Conditions
- Osteoarthritis
- Meniscus Tears
- Ligament Injuries
- Patellar Tendinitis
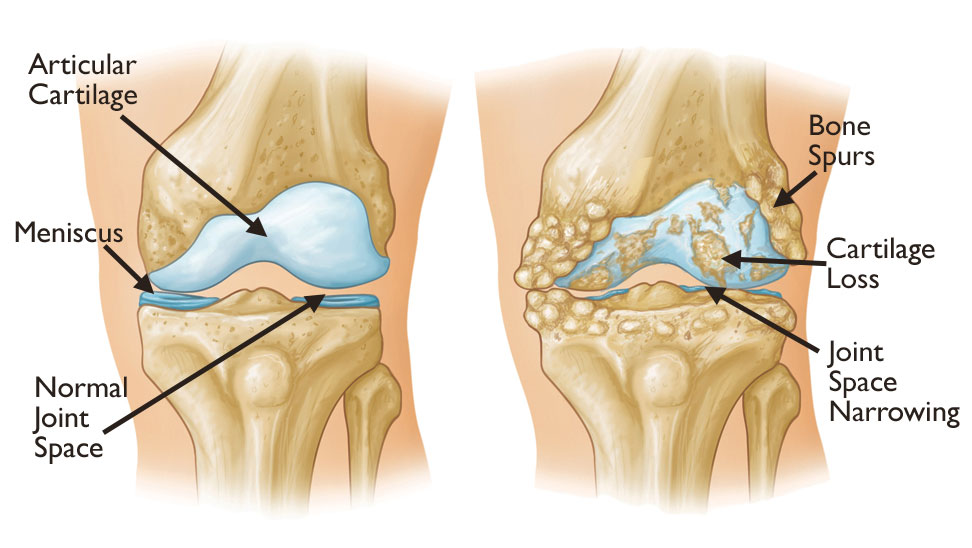
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis and a leading cause of knee pain. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. Symptoms include:
- Pain during or after movement
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity
- Loss of flexibility
- Swelling and tenderness
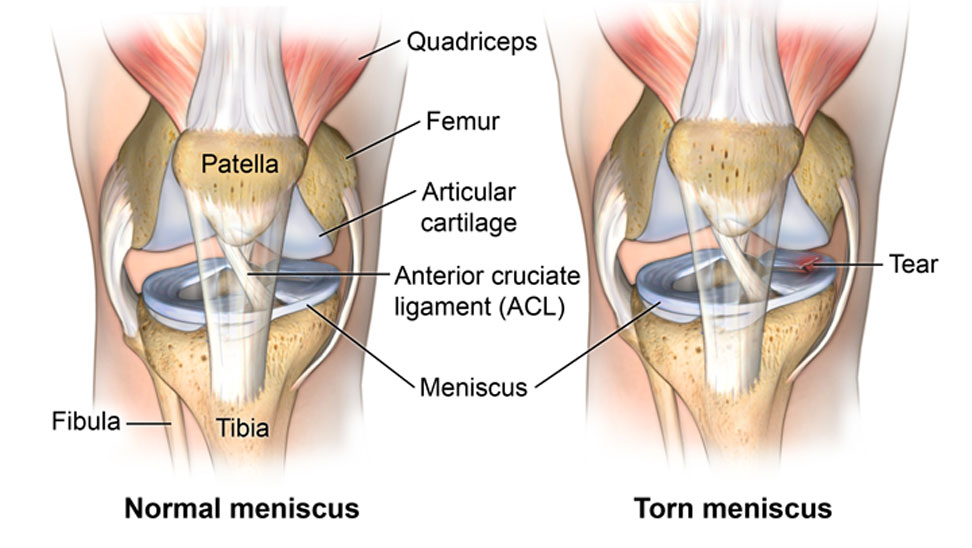
The meniscus is a piece of cartilage that acts as a shock absorber between your femur and tibia. A meniscus tear can occur due to a sudden twist or turn, often during sports activities. Symptoms include:
- Pain, particularly when twisting or rotating the knee
- Swelling and stiffness
- Difficulty straightening the knee fully
- A popping sensation at the time of injury
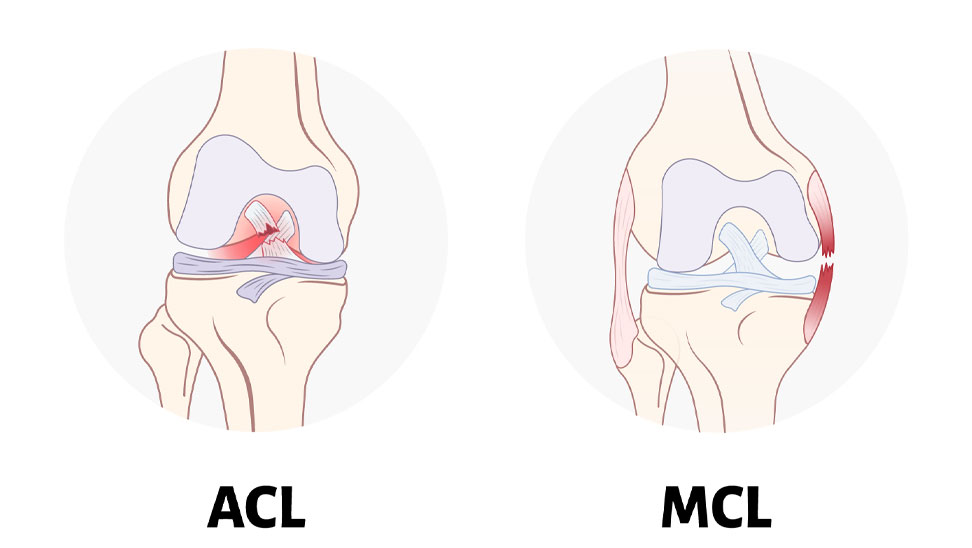
The knee contains four major ligaments: the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL), and lateral collateral ligament (LCL). Injuries to these ligaments, especially the ACL, are common in athletes and can result in instability and pain.
- ACL Injuries: Often occur during sports that involve sudden stops, jumps, or changes in direction. Symptoms include a loud pop during injury, severe pain, rapid swelling, and instability.
- MCL Injuries: Typically result from a direct blow to the outside of the knee. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and instability.
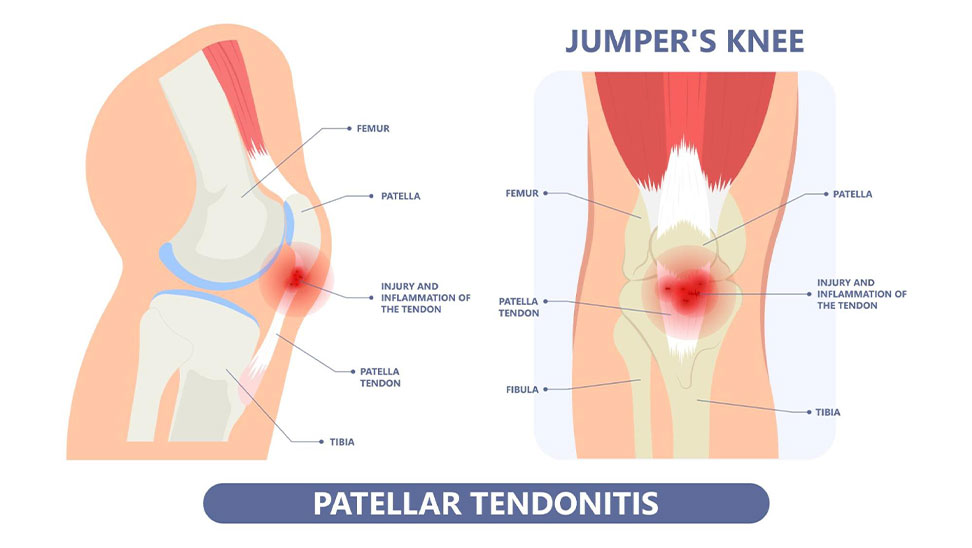
Also known as jumper’s knee, patellar tendinitis is an overuse injury affecting the tendon connecting the kneecap to the shinbone. It is common in athletes who engage in sports requiring frequent jumping. Symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness at the base of the kneecap
- Swelling
- Pain when jumping, running, or walking
- Stiffness and discomfort after physical activity
Who Require a Knee Replacement Surgery?
- Severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or post-traumatic arthritis causing debilitating pain and limited mobility.
- Chronic knee pain and stiffness unresponsive to conservative treatments.
- Significant knee deformity or alignment issues affecting daily activities.
- Failure of nonsurgical treatments such as medications, physical therapy, and injections.
- Desire to regain mobility and improve quality of life through surgical intervention.
Tests Required For Knee Replacement Surgery
- Routine Blood Tests
- X-ray
- MRI in certain cases
During The Knee Replacement Surgery
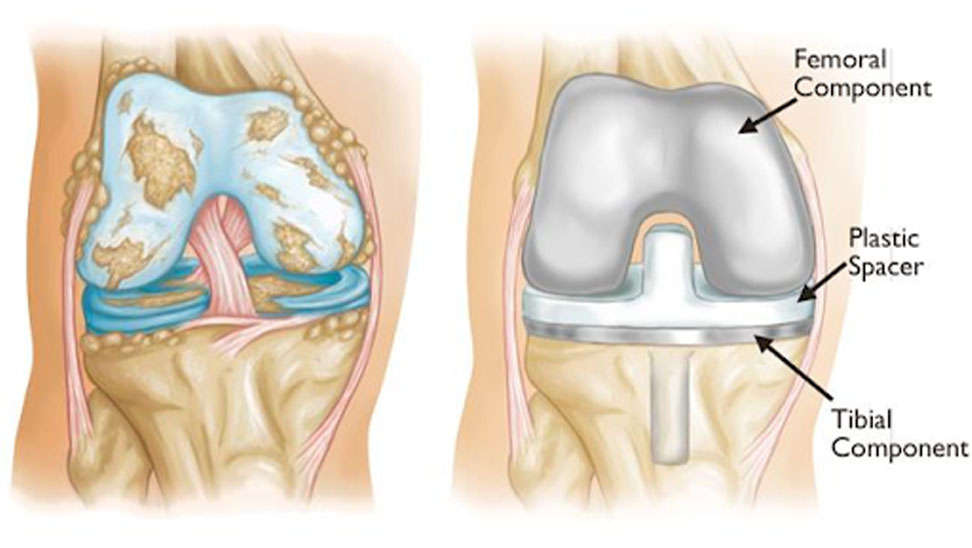
Following the incision, the surgeon carefully removes the damaged parts of the knee joint. The surgeon then places the prosthetic knee joint which is made up of metal and plastic.
After The Knee Replacement Surgery
A knee replacement surgery cannot be performed on an outpatient basis anywhere. It requires a hospital stay of three-four days. On the first day after surgery, the patient will meet with the physical therapist who will advise the patient to walk about with the help of crutches.
Physical therapy sessions following knee replacement surgery may be painful, but it is extremely important to follow them so that the new knees are able to function just as well as a healthy knee.
A Continuous Passive Motion machine (CPM) is used during one’s hospital stay. This device is attached to the affected leg and keeps surrounding areas of the knee in motion. This helps with speeding up recovery time and reducing post-operative complications.